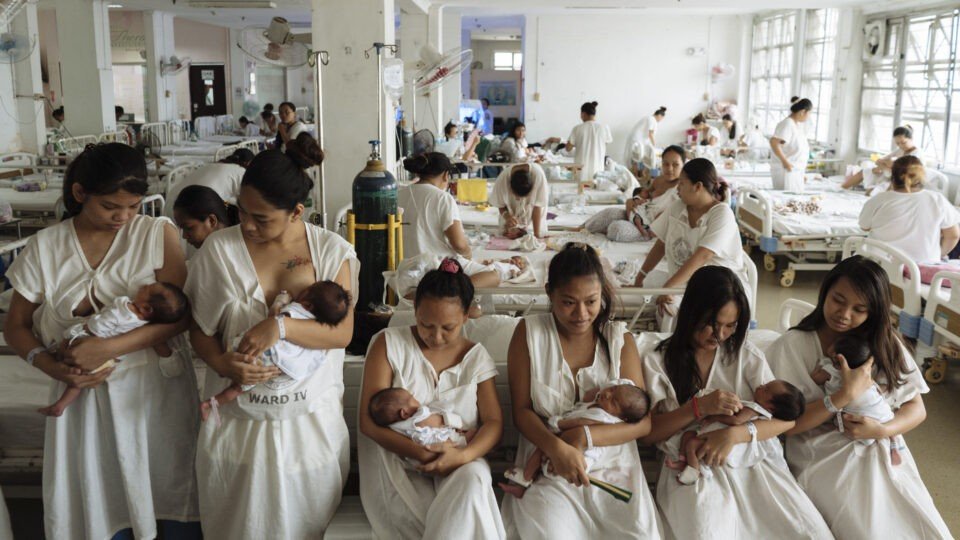
The baby factory
As we talk, the 41-year-old leans at an awkward angle, leveraging all her back strength to hold her ninth child in her arms.
“Carl, Jewel, Joyce…” As Rovelie names her children, six-year-old Charlie shoots his mother a look of disapproval. “Sorry, his name is Charlie,” says Rovelie, innocently.
Rovelie had had seven children before she learnt about family planning, but this latest addition was a surprise conceived during one of the world’s strictest lockdowns, which saw soldiers patrolling the streets in armoured personnel carriers, police checkpoints restricting movement and only one family member allowed out to shop for food supplies.
The lockdown also meant hundreds of thousands of women have been unable to access birth control, resulting in tales of unplanned pregnancies like Rovelie’s being repeated across the country.
Indeed, it is estimated an extra 214,000 unplanned babies will be born in the next year, according to projections by the University of the Philippines Population Institute and the United Nations Population Fund. These children will be born into hospitals already overwhelmed by 1.7 million births a year, largely into families struggling to make ends meet.
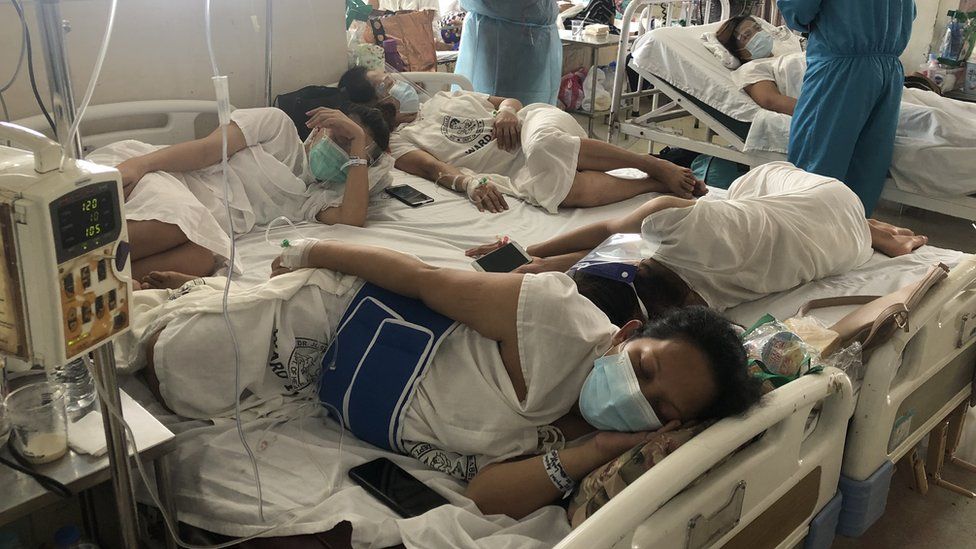
And this is only the start.
Because the pandemic isn’t the only reason why the Philippines has a population crisis on its hands – a closer look reveals a problem years in the making.
Staff at Dr Jose Fabella Memorial Medical Hospital are used to being busy. Back in 2012 the hospital delivered up to 120 babies a day, leading to the ageing, US-colonial-era maternity ward being dubbed “The Baby Factory”.
Things had improved, with the number falling to roughly half that since RHL was approved in 2012. But now they are readying themselves for the “baby boom”.
bbc uk




