The first new treatment for Alzheimer’s disease for nearly 20 years has been approved by regulators in the United States, paving the way for its use in the UK.
Aducanumab targets the underlying cause of Alzheimer’s, the most common form of dementia, rather than its symptoms.
At least 100,000 people in the UK with a mild form of the disease could be suitable for the drug.
But approval from the UK regulator could take more than a year.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) said there was “substantial evidence that aducanumab reduces amyloid beta plaques in the brain” and that this “is reasonably likely to predict important benefits to patients”.
Charities have welcomed the news of a new therapy for the condition – but scientists are divided over its potential impact because of uncertainty over the trial results.
In March 2019, late-stage international trials of aducanumab, involving about 3,000 patients, were halted when analysis showed the drug, given as a monthly infusion, was not better at slowing the deterioration of memory and thinking problems than a dummy drug.
But later that year, the US manufacturer Biogen analysed more data and concluded the drug did work, as long as it was given in higher doses. The company also said it significantly slowed cognitive decline.
Aducanumab targets amyloid, a protein that forms abnormal clumps in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s that can damage cells and trigger dementia, including:
- memory and thinking problems
- communication issues
- confusion
‘Heading in right direction’
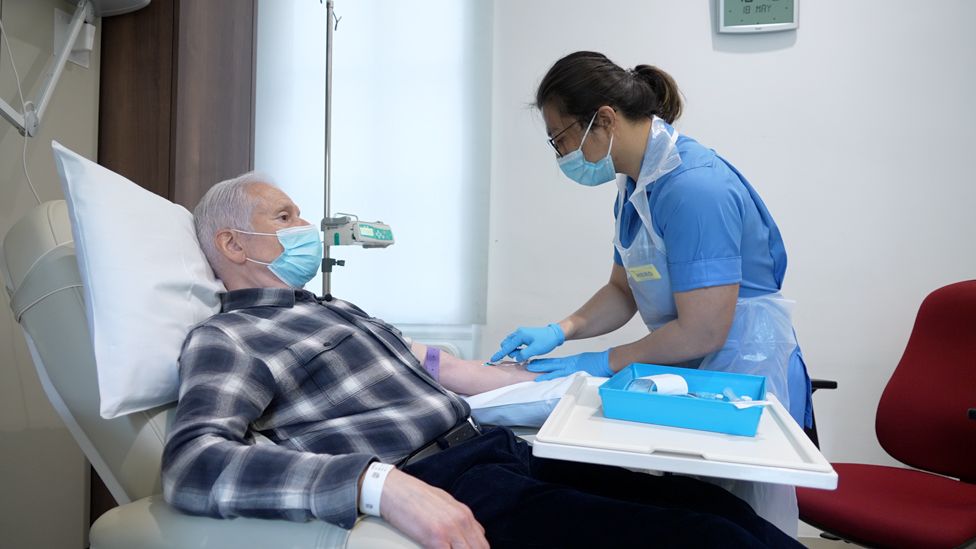
Aldo Ceresa, who took part in the trial, first noticed problems differentiating between left and right 10 years ago.
After his diagnosis, the 68-year-old, who is originally from Glasgow and now lives in Oxfordshire, close to his family, had to give up his job as a surgeon.
Mr Ceresa took aducanumab for two years before the trial was halted – and then had to wait almost as long for another trial, at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, in London, to begin.
“I’m quite happy to volunteer,” he says.
“I really, really enjoy this journey that I’m going through – and obviously the benefits I’m getting from it, which I’m very, very grateful for.
He is convinced the drug has helped him.
“I feel like I’m not quite as confused. Although it’s still there, it’s not quite as bad.
“And I’m just getting that bit more confident now.”
Mr Ceresa says his family has noticed improvements too.
“Before, if I was going to get something, I couldn’t remember, you know, where to find things in the kitchen.
“That has become less of a problem,” he says.
“And so, you know, it’s not 100% there – but I’m getting better at it.
“I haven’t caught up to the level that I was before – but I’m heading in the right direction.”
More than 30 million people around the world are thought to have Alzheimer’s, with most aged over 65.
For around 500,000 people affected in the UK, those eligible for aducanumab will:
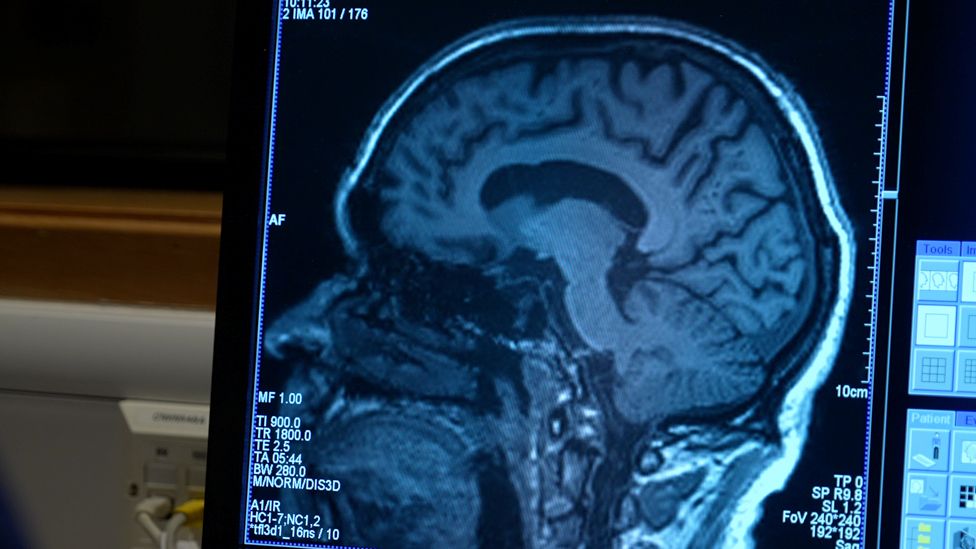
- probably require a definitive diagnosis, involving a detailed 3D brain scan
- be mostly in their in their 60s or 70s and at an early stage
In the past decade, more than 100 potential Alzheimer’s treatments have flopped.
Prof Bart De Strooper, director of the UK Dementia Research Institute, said the decision marked “a hugely significant milestone” in the search for treatments for Alzheimer’s disease.
But while he hoped it would prove a turning point for millions of people with the condition, he said there were “still many barriers to overcome including cost, eligibility and clinicians’ enthusiasm to prescribe a medicine whose effects are far from certain”.
Prof John Hardy, professor of neuroscience at University College London, said: “We have to be clear that, at best, this is a drug with marginal benefit which will help only very carefully selected patients.
“We will need better amyloid drugs down the line,” he added.
Although many doctors are doubtful of aducanumab’s benefits, its US approval will be a huge boost to dementia research, which is traditionally underfunded compared with cancer or heart disease.
bbc





